Saudi Astronauts Deliver First Space Research Breakthrough

Saudi Astronauts Deliver First Space Research Breakthrough-
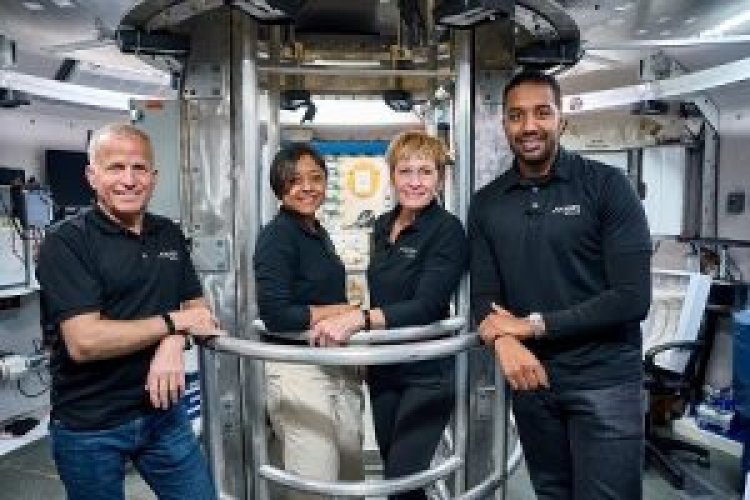
Saudi Arabia’s first human spaceflight mission has delivered its initial scientific breakthroughs, with 11 research papers and one patent emerging from experiments conducted aboard the International Space Station (ISS), the Saudi Space Agency (SSA) announced.
The findings stem from SSA-HSF1, the Kingdom’s landmark space mission launched in 2023. During the mission, Saudi astronauts carried out 19 scientific experiments in microgravity across three primary research tracks: biomedical sciences, human health, and science and technology. Several of the studies were conducted in collaboration with leading local and international research institutions, while additional results remain under analysis.
Breakthroughs in Biomedical Research-
In the biomedical sciences track, researchers successfully measured blood-based biomarkers to evaluate human health in space. One of the mission’s most notable achievements was the production of a high-precision nanomaterial designed for cartilage repair, which exceeded quality standards typically achieved in Earth-based laboratories.
The mission also marked a historic milestone with the first gene-transfer experiment involving stem cells conducted in space. This achievement opens new possibilities for regenerative medicine and advanced biological research in microgravity environments.
Advances in Human Health Studies-
Health-focused experiments examined the effects of short-duration spaceflight on the human brain. Researchers studied changes in intracranial pressure, optic nerve sheath diameter, cerebral perfusion, and brain electrical activity. In addition, scientists analyzed telomere length to better understand cellular ageing in microgravity.
These studies contribute valuable insights into spaceflight-associated neuro-ocular syndrome (SANS) and broader neurological health challenges faced by astronauts, while also offering potential benefits for medical research on Earth.
Science and Technology Experiments-
Within the science and technology track, a cloud-seeding experiment using a novel technique demonstrated efficient reactions between water vapour and silver iodide in microgravity. The results provide new understanding of how gravity influences condensation processes.
These findings may have practical applications for improving water security on Earth, as well as supporting future exploration missions to the Moon and Mars.
A Milestone for Saudi Space Ambitions-
Acting CEO of the Saudi Space Agency, Dr. Mohammed Al-Tamimi, said the results represent a significant milestone in the Kingdom’s scientific journey.
“These outcomes reflect Saudi Arabia’s commitment to advanced research, innovation, and international collaboration, in line with Vision 2030,” he said.
The Saudi Space Agency confirmed that work is ongoing on the remaining experiments from the SSA-HSF1 mission. Additional results are expected to be announced at regional and international scientific forums, further strengthening Saudi Arabia’s position as an emerging hub for space science and technology.